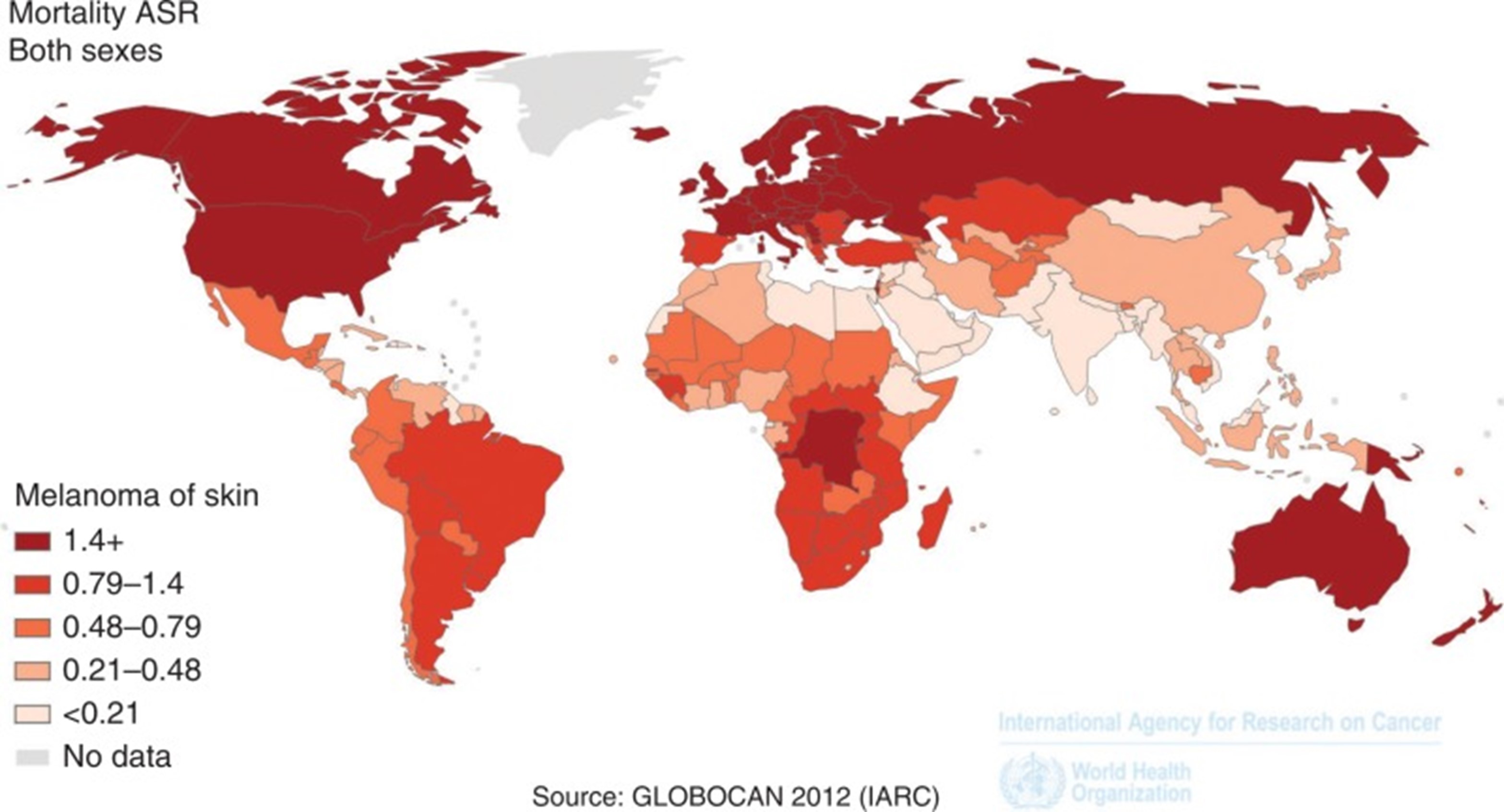
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the world.
According to media, more than 9.000 people are diagnosed with skin cancer every day in the US. 100.000 new cases of skin cancer diagnosed in France every year. In Australia, 2 in 3 people will get skin cancer in their lifetime. The annual treatment cost is estimated at $8,1B in the US and €236M in France.
Skin cancer rate increased 5-fold since 1970s and continues to increase in many places. In the meanwhile, there is an important lack of dermatologists, which leads to very long waiting time for patients and overwork for doctors.
Skin cancer at late stage often spreads to internal organs and becomes fatal. However, skin cancer at early stage can be cured with very high survive rate. Therefore, the key treatment is to detect skin cancer as soon as possible.
With the current lack of dermatologists all around the world, many people may have skin cancer without knowing it. The late skin cancer detection results in huge treatment cost, suffering for patients, and in many cases, the death that would be saved if being detected earlier.
Artificial Intelligence applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an advanced technology that has been transforming the world and every walk of life. It has changed much the way people think and make decision. It enables people to integrate information and analyse data more efficiently, hence improve decision making. AI has various applications in finance, health care, national security, transportation, entertainment, and so on.
The application of AI in health care has been accelerated since 2020s. Medical chatbots, robotic surgeries, virtual nursing assistants are some of such amazing applications. In skin care, AI has been used for classifying skin diseases or scoring severity of inflammations such as acne, psoriasis and so on.
Skin cancer detection powered by AI
The use of AI for skin cancer detection has received a tremendous attention recently. The ISIC challenge, biggest international competition for melanoma detection, has attracted many thousand participants from both industry and academia all around the world since its first launching in 2016.
Torus AI (formerly Torus Actions), the second winner of the ISIC challenge 2019, is a French start-up that has been developing several AI solutions for skin care, and in particular, for early skin cancer detection. Thanks to the success of its Skin Cancer AI, Torus AI has become one among 19 partners of iToBoS project, one of biggest European projects for fighting skin cancer.
iToBoS (Intelligent Total Body Scanner for Early Detection of Melanoma) project is funded by European Research Council Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 965221. The goal of the project is to build a full-body 3D scanner that can be used in hospitals for early detection of melanoma and other types of skin cancer. The project has a duration of 48 months (1 April 2021-31 March 2025) and a total Budget of 12 million Euro, with 19 members, including universities and hospital, large companies, NGOs and small companies.
The role of Torus AI in iToBoS project is developing AI solution for automatic mole detection, mole matching, UV damage scoring, and essentially, skin cancer detection. In the Task 8.5, Torus AI works on developing AI for mole classification and provide image-based cancer risk assessment.
Skin Cancer AI for early melanoma detection
The current Skin Cancer AI developed by Torus AI can detect up to 12 types of melanomas (the most deadly skin cancer), 38 types of non-melanoma skin cancer, and over 70 types of other pre-cancer or benign skin lesions. This AI also provides a cancer risk index which range from 0 to 5 for very benign to very malignant or high-grade cancer.
Here are examples of melanoma detection using Skin Cancer AI.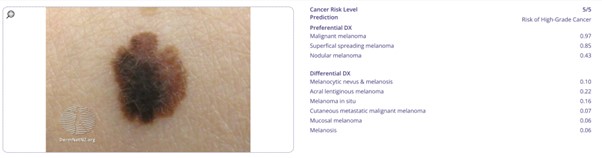
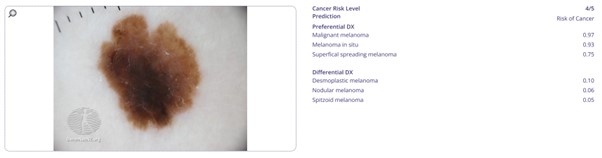
The clinical and dermoscopic images are taken from DermnetNZ, one of the most reliable websites for skin disease information. The two images are taken for a same lesion which is melanoma in situ, a kind of early-stage melanoma. The AI detected high cancer risk for both images, and in particular, detected melanoma in situ with high confidence using dermoscopic image.
With the financial support of European Council, iToBoS project will bring the best value of AI to assist doctors in diagnosis and improve skin cancer detection in Europe and all around the world. This will help save lives, save time, save money, that benefits to all patients, doctors, and national health care systems.
